We are living in the golden days of robotics. Collaborative robot offers numerous potential opportunities for enterprises in developing nations at first, but the problems they will confront are significant. The deployment of Cobot, which possesses the most advanced technology, is a major worry for enterprises in nations with little science and technology.
Despite the rise of collaborative robot, artificial intelligence, and other developing technologies and the supposed threat of job losses that comes with it, the global economy is still growing. Even in a recession, unemployment is historically low.
Most people fail to understand that the introduction of collaborative robots isn’t a battle between man and machine. Rather, we are on the brink of entering the next phase of the automation economy, with tremendous value derived from the partnership of man and machine.
The automated economy has far-reaching implications outside the labor market, with considerable benefits for businesses, individuals, the economy, and society.
Cobot promotes production for manufacturing industries
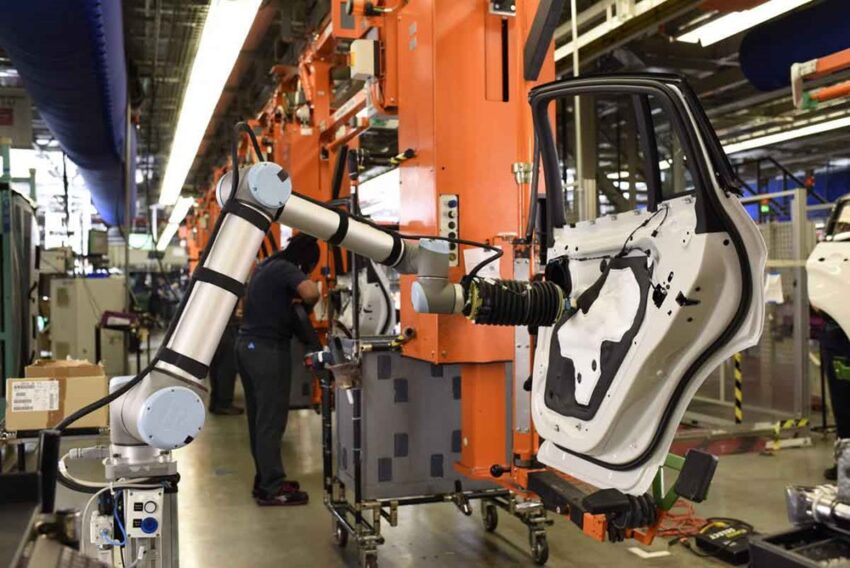

The process of introducing the future collaborative robot in manufacturing industries is underway. However, this makes a lot more sense, in third world countries.
At the moment, half of developing countries are responsible for supplying industrial goods to the world market.
This means that industrial output in these economies is under pressure to meet both local and international demand.
The foundation of all successful companies is built on strong supply chains and efficient logistics management. Economies thrive through producing goods or providing services to other firms and customers. What role do robots play in these businesses’ production? What advantages do robots provide?
Here are a few examples of how robots can assist companies now and in the long term:
1. Increased Productivity

Manufacturing plants and warehouses significantly improve efficiency when machines do the heavy lifting.
Cobots are taught to perform repetitive activities and spend far less time on them than humans. Whether it is a collaborative robot packing items or self-driving machine moving pallets, the industrial process has become more efficient.
2. Improved workplace safety
Workers in the ironwork and construction industry face many safety risks in their daily activities. Despite having safety and standard procedures, there’s no way to guarantee employees full protection against accidents. Collaborative robots can perform these tasks efficiently and protect human life.
3. Higher productivity
A collaborative robot can work for an extended period without having a break. The resultant increased productivity enables businesses to serve their customers better.
4. Quality supply chain

For companies to stay competitive in the market, supply chains need to run consistently. The recent pandemic significantly affected the supply chain when workers were laid off. Every element of the supply chain is interdependent; when one component fails, the whole framework is negatively affected. Robots come in handy in such events by ensuring everything runs smoothly in all aspects of the industry.
5. Growth in Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
Increased productivity directly triggers the growth of Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Studies indicate AI could generate an additional US$13 trillion in economic output by 2030, raising global GDP by 1.2 percent every year. This is because the substitution of labor by Cobots increases innovation in the product and service sector.
6. Creating Jobs

Many people fail to appreciate the role of Cobots in creating new, high-paying opportunities that demand highly competent employees. While it is obvious that robots are substituting low-skilled employees and automating their duties, robots and automation are necessitating jobs that shift the focus of workers to higher-value tasks.
For instance, robots can undertake basic activities like sorting raw materials, shipping, and packing in the manufacturing industry. At the same time, higher-skilled individuals can accomplish tasks like quality-related duties, which humans are better suited for.
While it is true that Cobots are displacing human labor across all job categories, there has never been a better opportunity for workers to advance their skills to undertake higher-paying positions.
7. Promoting healthy competition
Adapting collaborative robots in developed and developing economies means the production process is uniform across all industries. This leads to the similarity in quality and quantity of output, promoting healthy competition.
8. Improves working environment
The ability of Cobots to replace the human workforce in delicate sectors of the industry has created confidence in workers. By supporting employees to complete their tasks with optimum productivity, morale is boosted, and workers start enjoying their working environment.
It is just a matter of time before employees start seeing the essence of Cobots and appreciating the fact that the manufacturing industry is entering a new phase.
9. Customization
Automation results in greater economic scope. This means that a single plant may manufacture a wider range of goods; product diversification and diversity are just as crucial as lower unit labor costs for businesses. The goal in the 1950s was to make items as cheaply as possible.
Consumers are now searching for more product customization. Instead of purchasing a conventional model off the manufacturing line, automation allows buyers to customize their desired product’s size, design, and operation.
10. Economies of scale
Collaborative robots enable companies to produce goods and services at low costs translating to significant economies of scale. This is essential for industries that need high capital.
Consequently, many investors will be encouraged to open up more industries that will employ citizens and generate revenue for the government. Moreover, more industries mean more amenities and development in regions where these industries have been set up.
Bottom line
When businesses succeed, they provide greater opportunities for employees and the general public. New technologies not only replace labor with robots but also cut prices in a competitive market. Furthermore, technology may enhance product quality, customization, or delivery speed. All of these factors raise demand. Even if the labor required per unit of output decreases, if demand rises sufficiently, employment will expand.
The social benefits of collaborative robots include better earnings, lower prices for goods, and higher tax revenue for countries.
While there will be challenges along the way, the automated economy is a win-win situation for all parties involved, with benefits such as new job creation, societal improvement, and economic growth.

